Open Source
Bolted Connection
On Github: Example Bolted ConnectionIn this Example we will do a simple bolted connection.First we need to create the geometry.
#!cubitresetcreate brick x 40 y 20 z 5volume 1 copy move x 20 z -5.001create cylinder height 11 radius 4move volume 3 x 10 z -2.5 include_mergedcreate cylinder height 4 radius 6move volume 4 x 10 z 4.501 include_mergedcreate cylinder height 4 radius 6move volume 5 x 10 z -9.502 include_mergedsubtract volume 4 from volume 3 keep_toolsubtract volume 5 from volume 3 keep_toolcreate cylinder height 20 radius 4.25move volume 6 x 10 z -2.5 include_mergedsubtract volume 6 from volume 1 2
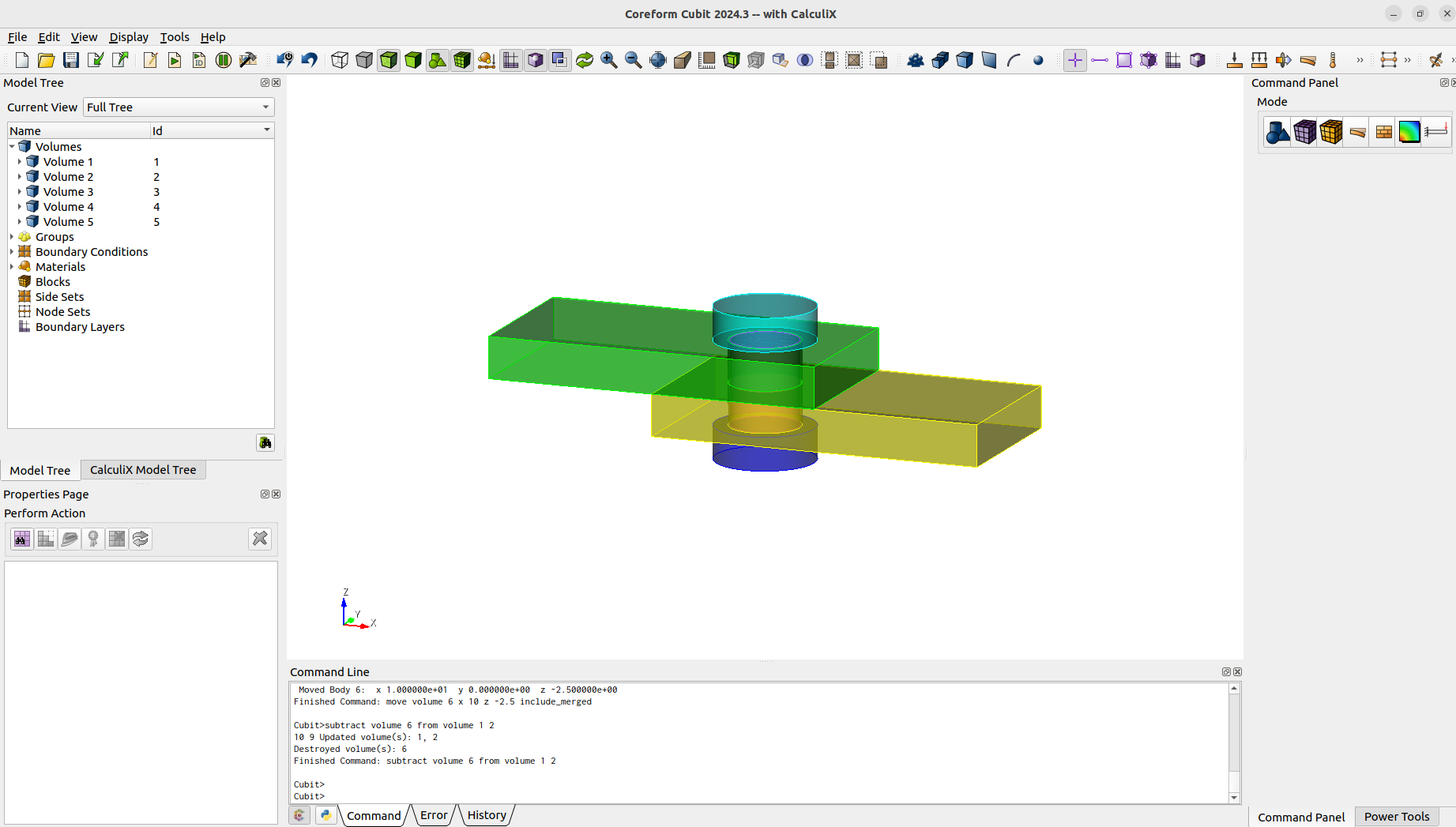
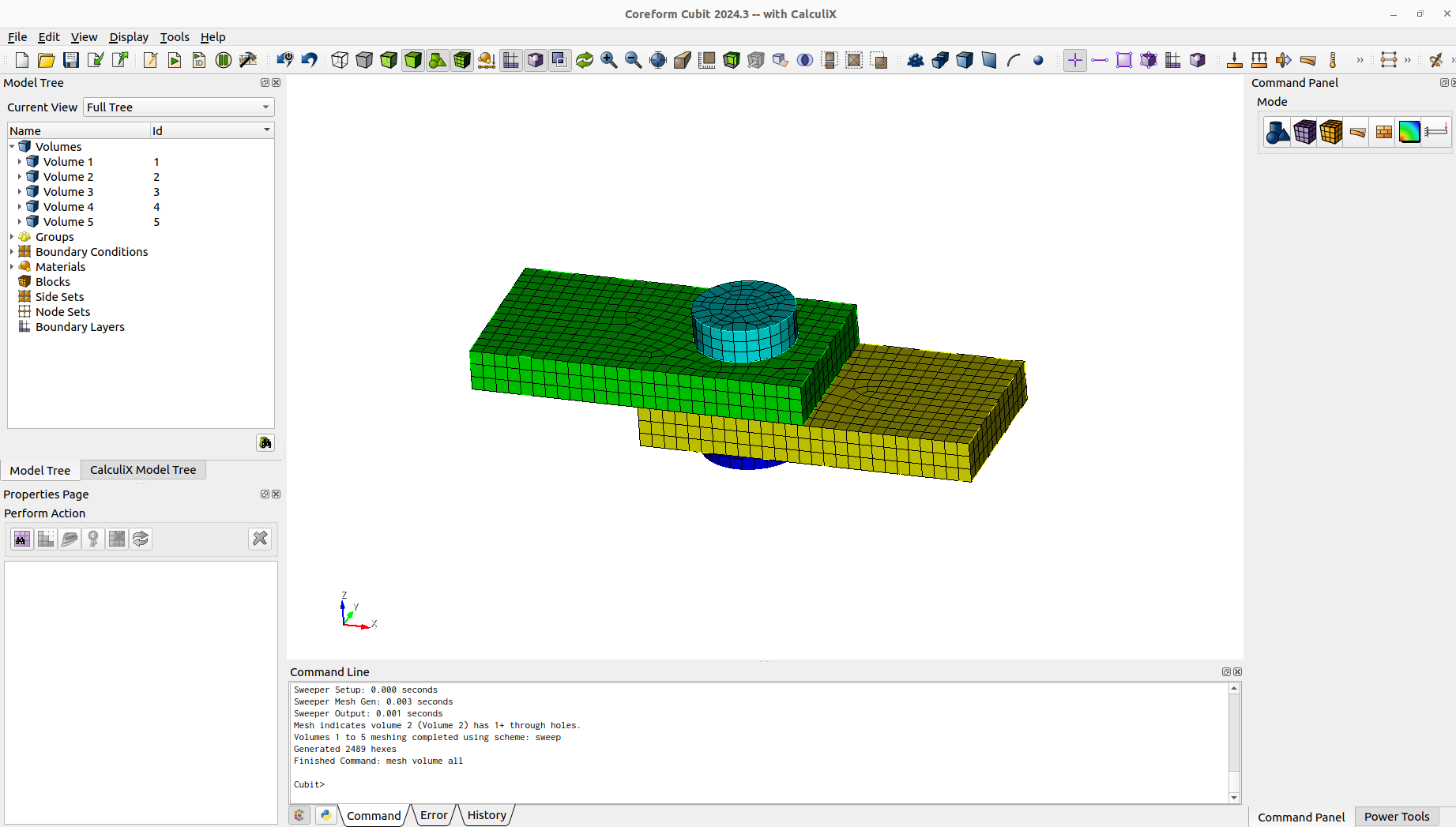
After the geometry creation we can already imprint, merge and mesh.
imprint vol allmerge vol allmesh vol all
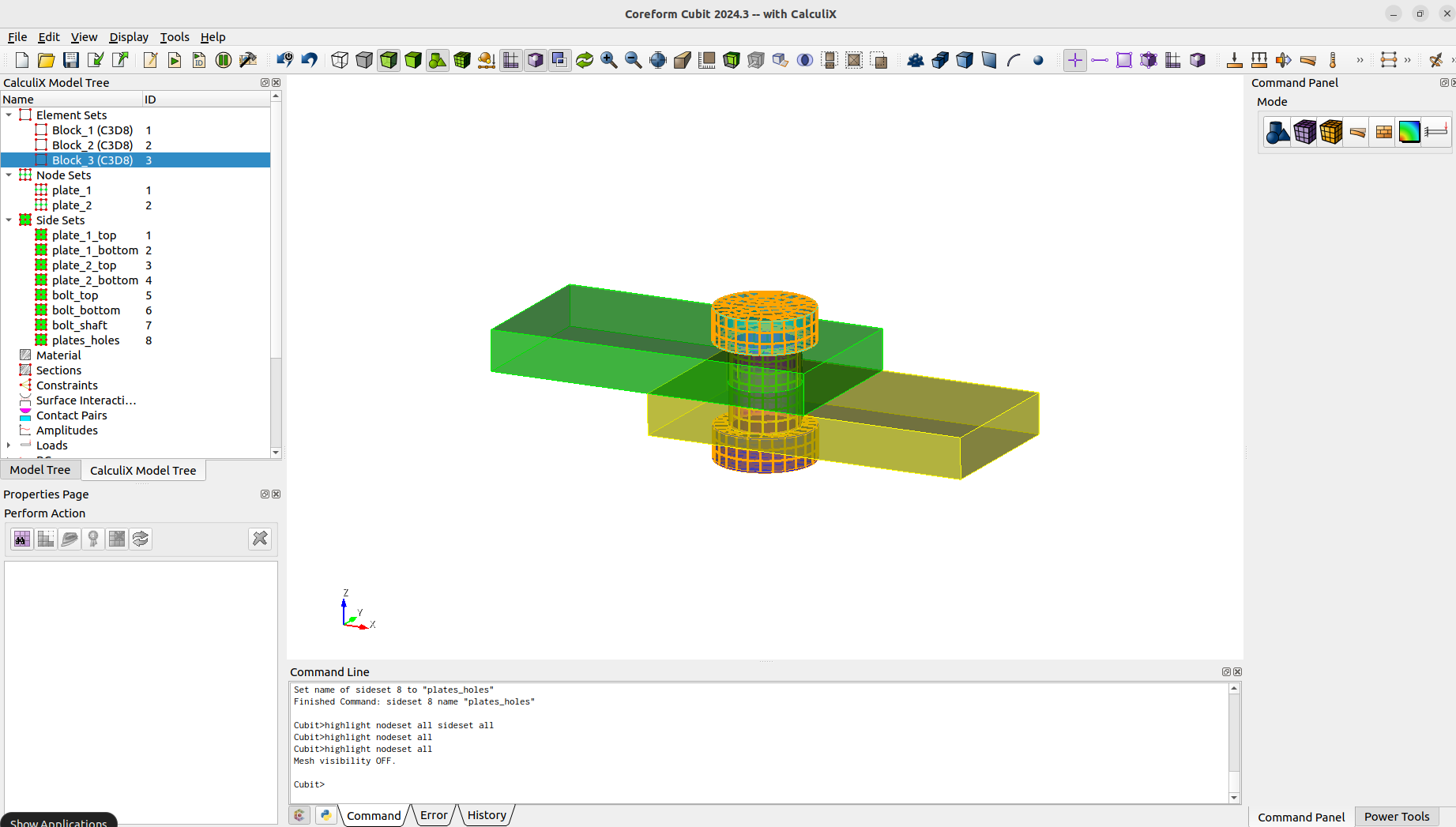
We define the blocks (element sets), nodesets and sidesets that will be needed.
block 1 add vol 1block 2 add vol 2block 3 add vol 3 to 5nodeset 1 add surface 4nodeset 1 name "plate_1"nodeset 2 add surface 12nodeset 2 name "plate_2"sideset 1 add surface 30sideset 1 name "plate_1_top"sideset 2 add surface 31sideset 2 name "plate_1_bottom"sideset 3 add surface 33sideset 3 name "plate_2_top"sideset 4 add surface 34sideset 4 name "plate_2_bottom"sideset 5 add surface 36sideset 5 name "bolt_top"sideset 6 add surface 38sideset 6 name "bolt_bottom"sideset 7 add surface 25sideset 7 name "bolt_shaft"sideset 8 add surface 29 32sideset 8 name "plates_holes"
We define the material and make a section assignment.
create material "steel" property_group "CalculiX-FEA"modify material "steel" scalar_properties "CCX_ELASTIC_USE_CARD" 1modify material "steel" scalar_properties "CCX_ELASTIC_ISO_USE_CARD" 1modify material "steel" matrix_property "CCX_ELASTIC_ISO_MODULUS_VS_POISSON_VS_TEMPERATURE" 2.1e+5 0.3 0modify material "steel" scalar_properties "CCX_PLASTIC_ISO_USE_CARD" 1modify material "steel" scalar_properties "CCX_DENSITY_USE_CARD" 1modify material "steel" matrix_property "CCX_DENSITY_DENSITY" 7.85e-06 0modify material "steel" scalar_properties "CCX_EXPANSION_USE_CARD" 1modify material "steel" scalar_properties "CCX_EXPANSION_ISO_USE_CARD" 1modify material "steel" matrix_property "CCX_EXPANSION_ISO_A_TEMPERATURE" 1.2e-05 0modify material "steel" scalar_properties "CCX_PLASTIC_USE_CARD" 1modify material "steel" matrix_property "CCX_PLASTIC_ISO_YIELD_STRESS_VS_STRAIN_VS_TEMPERATURE" 235 0 0ccx create section solid block all material 1
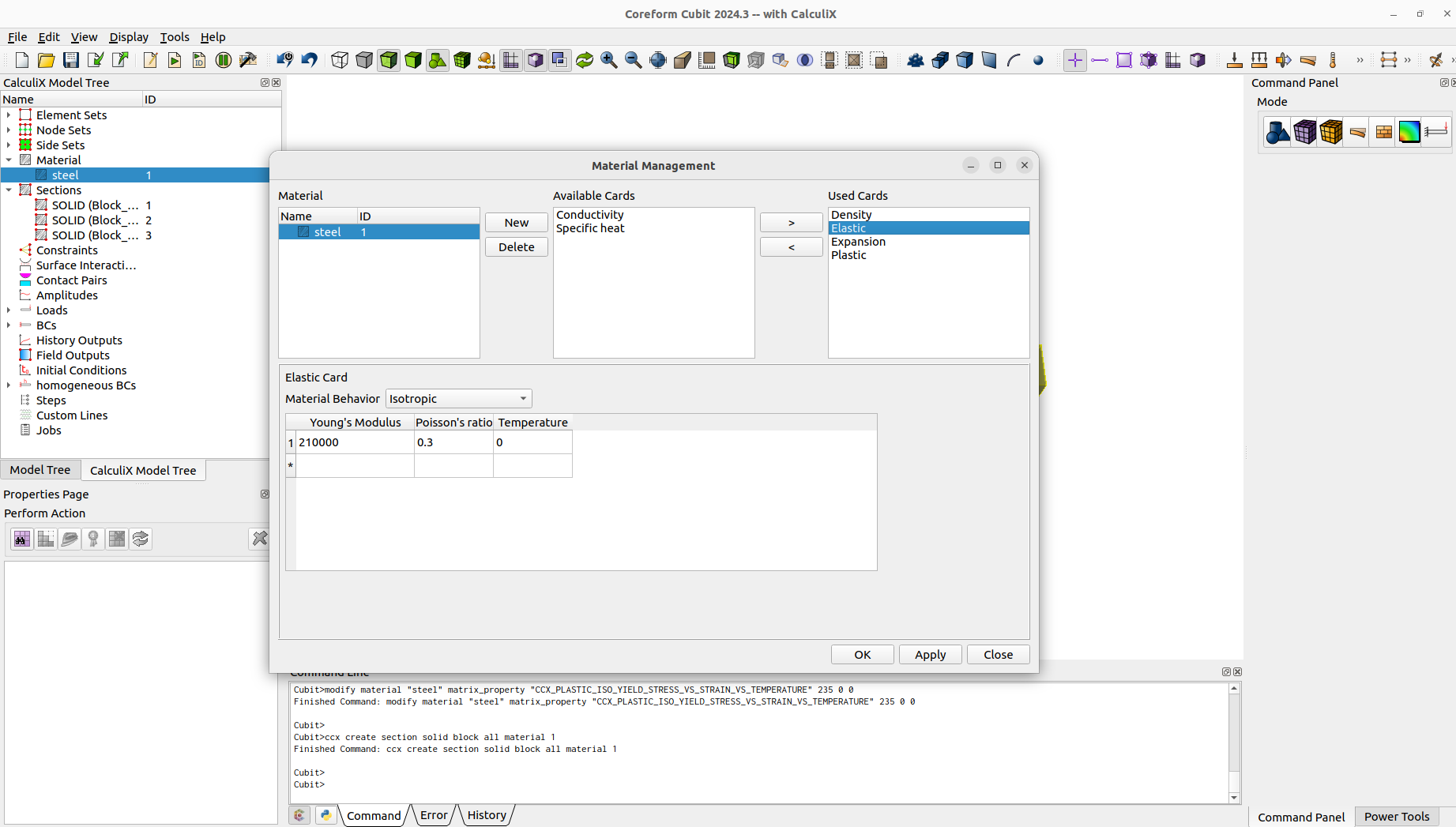
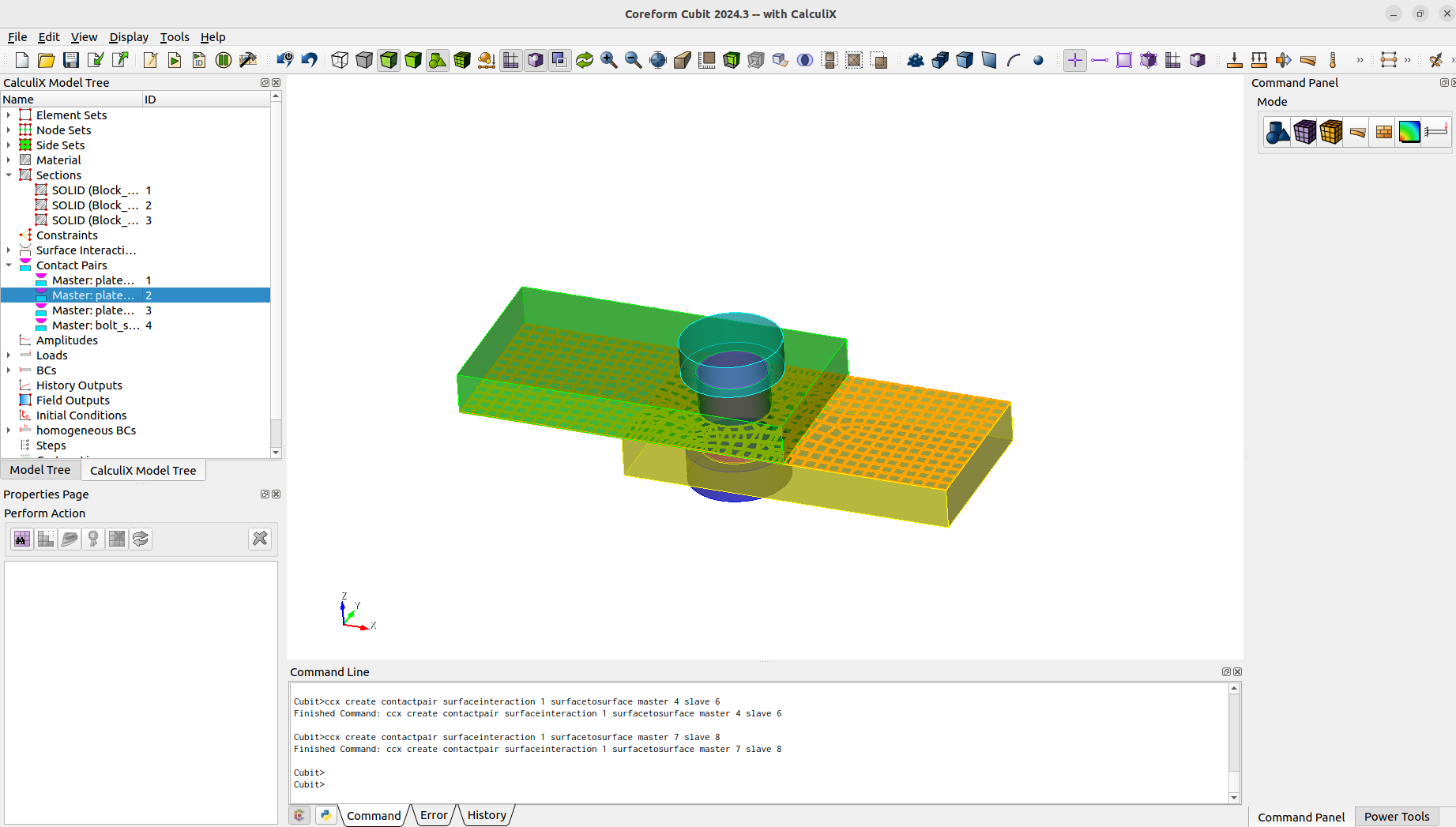
As we want to model a contact problem, we need a surface interaction and contact pairs.
ccx create surfaceinteraction name "interaction" linear slopeK 1e+7 sigmaINF 1 c0 1e-3ccx modify surfaceinteraction 1 friction mu 0.1 lambda 500ccx create contactpair surfaceinteraction 1 surfacetosurface master 1 slave 5ccx create contactpair surfaceinteraction 1 surfacetosurface master 2 slave 3ccx create contactpair surfaceinteraction 1 surfacetosurface master 4 slave 6ccx create contactpair surfaceinteraction 1 surfacetosurface master 7 slave 8
One way to define a preload for bolts, is to use the thermal expansion or in this case a shrinking. It is needed to define initialconditions for the temperature and "preload" the bolt with a temperature.
create temperature on volume all value 0ccx create initialcondition temperatureccx modify initialcondition 1 temperature bc_id 1#preloadcreate temperature on volume 3 value -50ccx modify temperature 2 keyword_type temp
To initial the contact we first want the plates to be fixed. When contact is achieved we will pull the plates apart. The boundary conditions are as follows.
# plate bccreate displacement name "plate_1_fix" on nodeset 1 dof 1 dof 2 dof 3 fix 0create displacement name "plate_2_fix" on nodeset 2 dof 1 dof 2 dof 3 fix 0create displacement name "plate_1_pull" on nodeset 1 dof 1 fix -0.35create displacement name "plate_2_pull" on nodeset 2 dof 1 fix 0.35
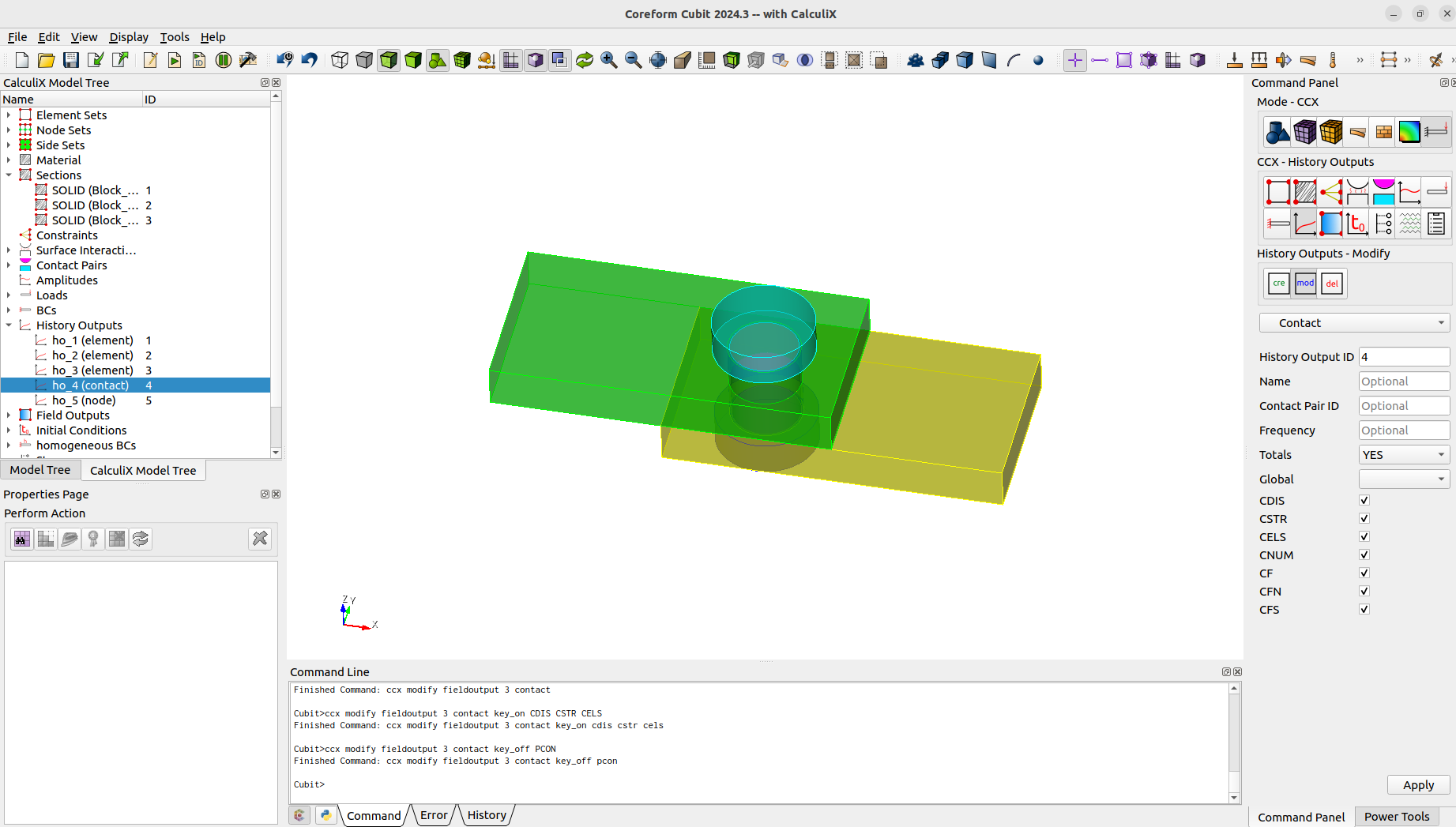
To get some results we need to define the history and field outputs.
ccx create historyoutput name "ho_1" elementccx modify historyoutput 1 element block 1 totals_yesccx modify historyoutput 1 element key_on S Eccx modify historyoutput 1 element key_off SVF ME PEEQ CEEQ ENER SDV HFL HFLF COORD ELSE ELKE EVOL EMAS EBHE CENTccx create historyoutput name "ho_2" elementccx modify historyoutput 2 element block 2ccx modify historyoutput 2 element key_on S Eccx modify historyoutput 2 element key_off SVF ME PEEQ CEEQ ENER SDV HFL HFLF COORD ELSE ELKE EVOL EMAS EBHE CENTccx create historyoutput name "ho_3" elementccx modify historyoutput 3 element block 3ccx modify historyoutput 3 element key_on S Eccx modify historyoutput 3 element key_off SVF ME PEEQ CEEQ ENER SDV HFL HFLF COORD ELSE ELKE EVOL EMAS EBHE CENTccx create historyoutput name "ho_4" contactccx modify historyoutput 4 contact contactpair 1 totals_yesccx modify historyoutput 4 contact key_on CDIS CSTR CELS CNUM CF CFN CFSccx create historyoutput name "ho_5" nodeccx modify historyoutput 5 node nodeset 1 totals_yesccx modify historyoutput 5 node key_on U RFccx modify historyoutput 5 node key_off NT TSF TTF PN PSF PTF MACH CP VF DEPF TURB MF RFLccx create fieldoutput name "fo_1" nodeccx create fieldoutput name "fo_2" elementccx create fieldoutput name "fo_3" contactccx modify fieldoutput 1 nodeccx modify fieldoutput 1 node key_on RF U NTccx modify fieldoutput 1 node key_off CP DEPF DEPT DTF HCRI KEQ MACH MAXU MF PNT POT PRF PS PSF PT PTF PU RFL SEN TS TSF TT TTF TURB V VFccx modify fieldoutput 2 elementccx modify fieldoutput 2 element key_on E Sccx modify fieldoutput 2 element key_off CEEQ ECD EMFB EMFE ENER ERR HER HFL HFLF MAXE MAXS ME PEEQ PHS SF SMID SNEG SPOS SVF SDV THE ZZSccx modify fieldoutput 3 contactccx modify fieldoutput 3 contact key_on CDIS CSTR CELSccx modify fieldoutput 3 contact key_off PCON
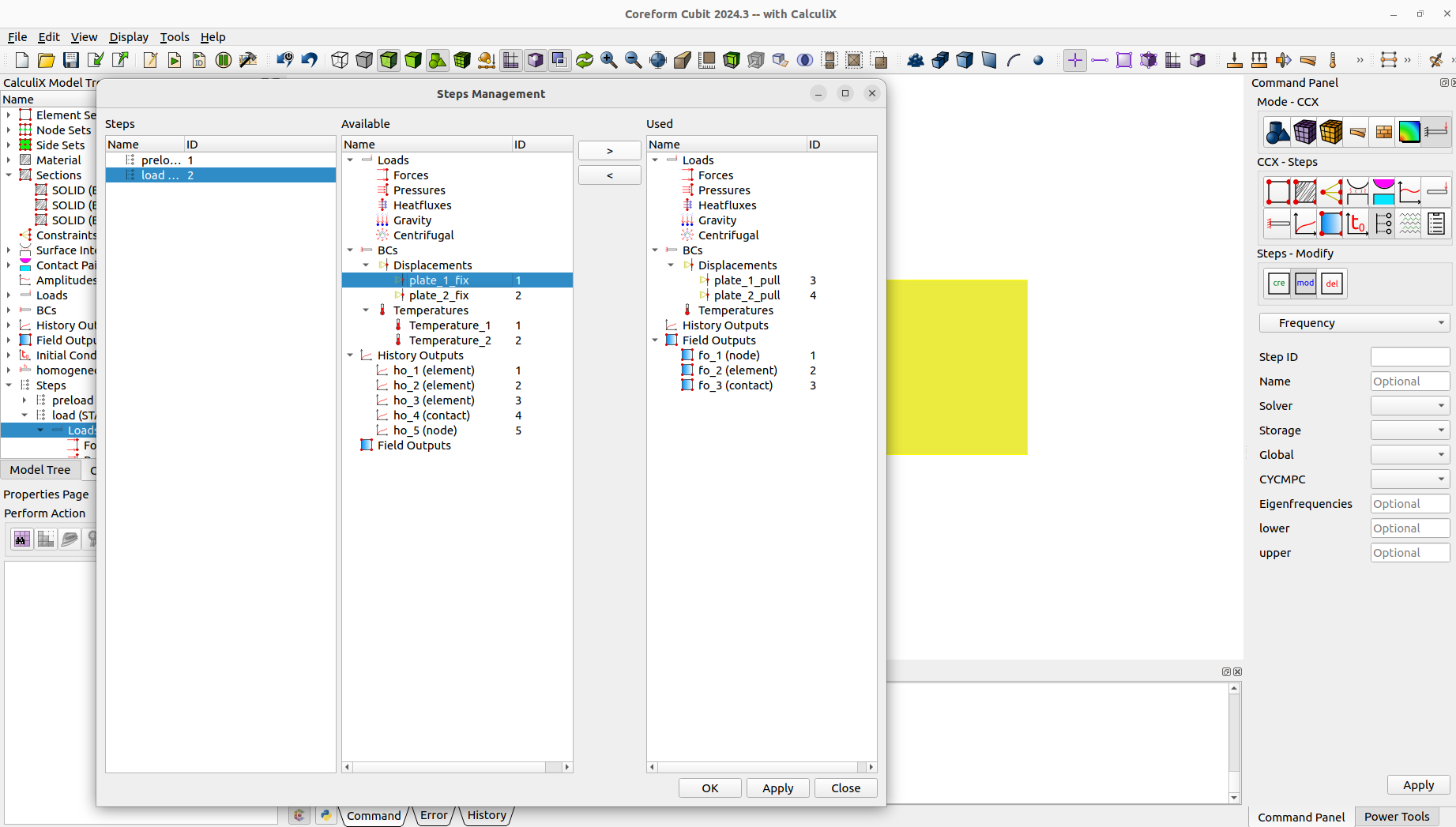
Now we define the two needed steps. First one is to preload the bolt and achieve contact. The second step is for pulling the plates apart. We can easily assign the bc's and outputs to the steps with the steps management.
ccx create step name "preload" staticccx modify step 1 parameter nlgeom_yesccx modify step 1 static totaltimeatstart 0 initialtimeincrement 0.5 timeperiodofstep 1 minimumtimeincrement 1e-5 maximumtimeincrement 0.5ccx step 1 add fieldoutput 1 2 3ccx step 1 add historyoutput 1 2 3 4 5ccx step 1 add bc temperature 2ccx step 1 add bc displacement 1 2ccx create step name "load" staticccx modify step 2 parameter nlgeom_yesccx modify step 2 static totaltimeatstart 1 initialtimeincrement 0.01 timeperiodofstep 1 minimumtimeincrement 1e-5 maximumtimeincrement 0.02ccx step 2 add fieldoutput 1 2 3ccx step 1 add historyoutput 1 2 3 4 5ccx step 2 add bc displacement 3 4
Last thing is to create a job and then we can already run CalculiX.
ccx create job name "bolted_connection"ccx run job 1
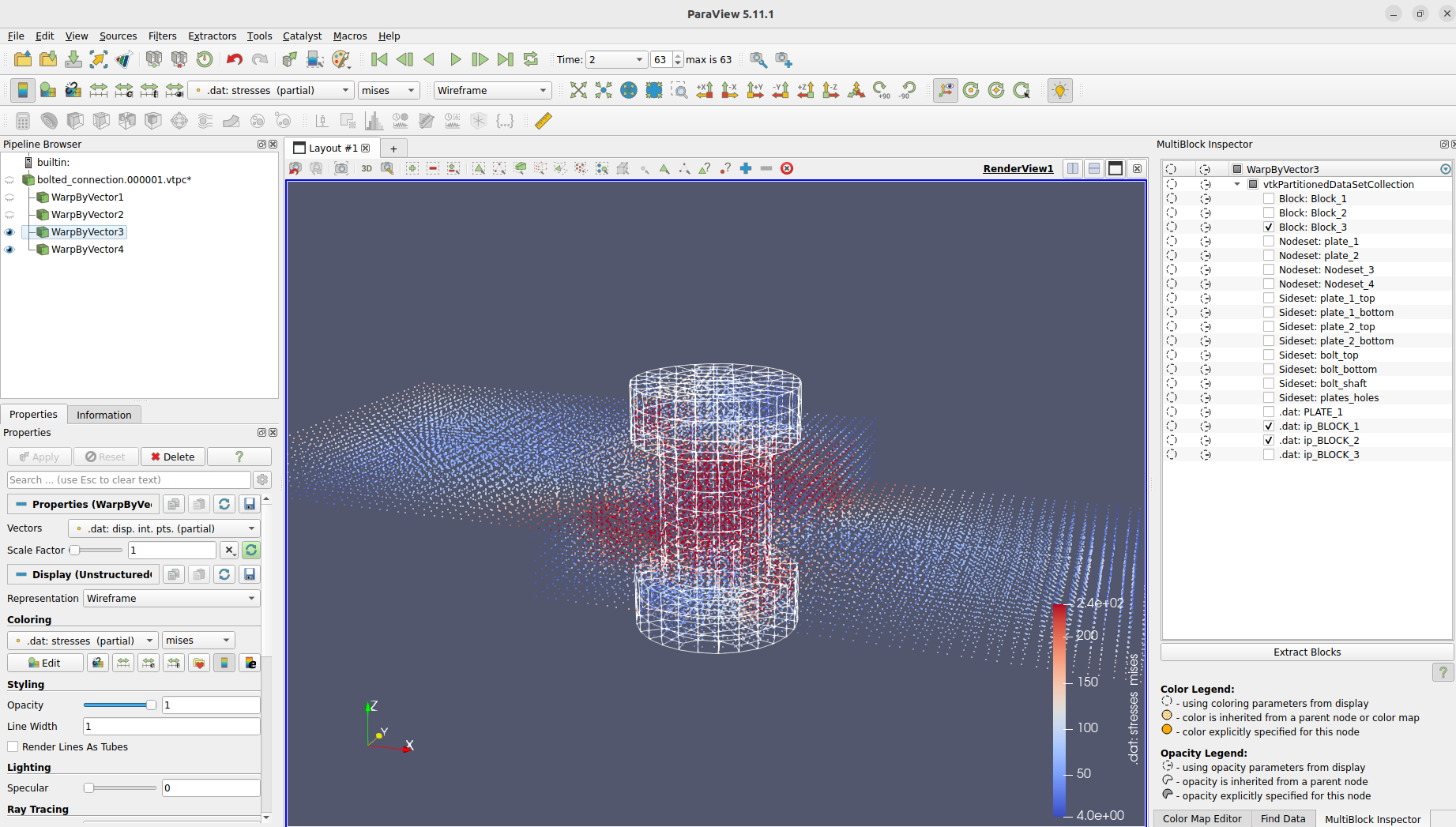
When we view the results with paraview. We will notice that some results from CalculiX were skipped in the conversion.
This is because we used a contact output. In the .frd file, contact outputs will only be written for elements in contact. This means that not for every node a result will exists. Inconsistent results over the iterations will cause problems, so they will be skipped when writing the data for paraview.To view the skipped results we will manually convert the results with the partial option. This way missing nodal results will be filled and marked and we can view the missing CalculiX results now in paraview.
ccx result convert job 1 partial
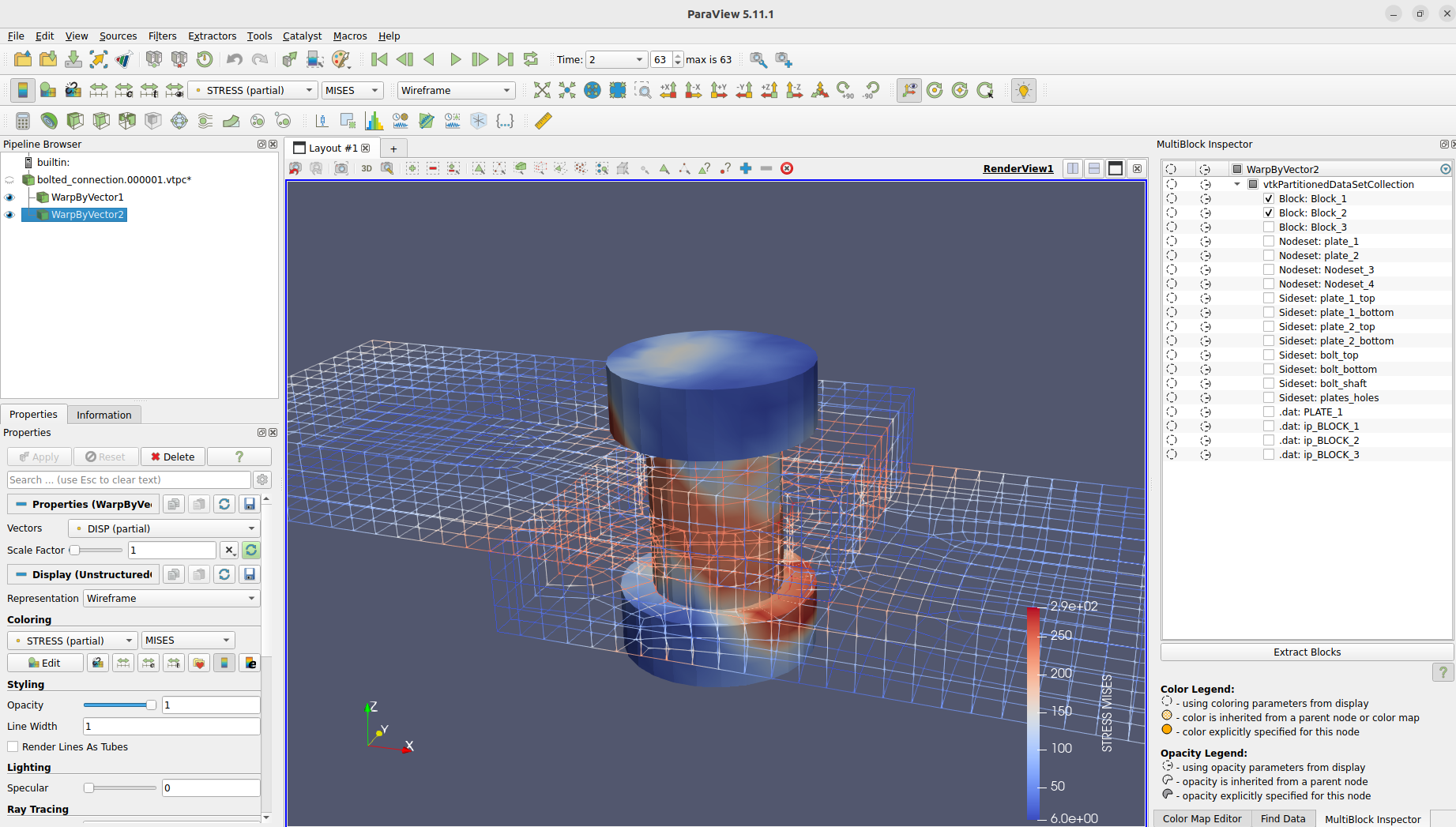
We can even take a look at the integration point results from CalculiX.